also known as
Clinostomum complanatum
Clinostomum marginatum
fluke
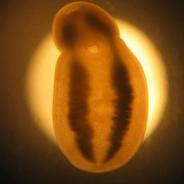
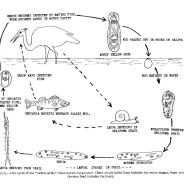
These worms appear as small, yellow cysts in the flesh or skin of fish. They are the immature or larval stage (metacercaria) of the parasite that when eaten by a bird (heron or bittern) develop into adult trematodes in the bird’s mouth or throat. The adult worms shed eggs which hatch in freshwater to form miracidia which then infect snails. The organisms multiply in the snail and form cercaria, which leave the snail and swim to find their next host, a fish, into which they burrow and encyst. Fish normally are unaffected by grubs unless they become heavily infected. Although unsightly, there is no health risk associated with eating the cooked flesh of infected fish.
Distribution
North America
Hosts
freshwater fish, common in warmwater species like bluegill, largemouth bass and catfish.
Detection Methods:
gross pathology / gross clinical signs